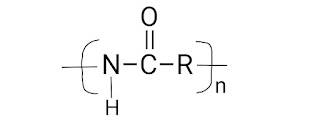
Types Of Addition Polymerization
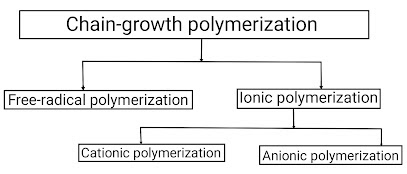
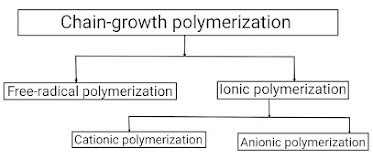
Chain-growth polymerization reaction is one of two processes to convert a monomer molecule into a polymer. Chain-growth polymerization reaction is a polymerization technique where unsaturated monomer (means containing double and triple bonds in their structural formula) molecules add onto the active site on a growing polymer chain one at a time. Depending on this active site present on the growing polymer chain, there are three types of addition polymerization: free radical polymerization , ionic polymerization , and coordination polymerization . Out of which, coordination polymerization is rarely observed, so we will not study about it. Thus, Let us study briefly about all these types of addition polymerization reactions; (A) Free radical polymerization – Free radical polymerization is defined as a type of addition polymerization in which the active centres are free radical. It is denoted as "M•". Since free radical polymerization is a type of ad...