Types Of Addition Polymerization
Chain-growth polymerization reaction is one of two processes to convert a monomer molecule into a polymer. Chain-growth polymerization reaction is a polymerization technique where unsaturated monomer (means containing double and triple bonds in their structural formula) molecules add onto the active site on a growing polymer chain one at a time.
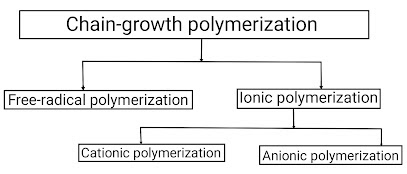
Depending on this active site present on the growing polymer chain, there are three types of addition polymerization: free radical polymerization, ionic polymerization, and coordination polymerization. Out of which, coordination polymerization is rarely observed, so we will not study about it. Thus,
Let us study briefly about all these types of addition polymerization reactions;
(A) Free radical polymerization–
Free radical polymerization is defined as a type of addition polymerization in which the active centres are free radical. It is denoted as "M•". Since free radical polymerization is a type of addition polymerization reaction, it also occurs in three steps as addition polymerization; initiation, propagation and termination.
Chain initiation
In this, first the initiator is converted into intermediate with the help of light, heat or catalyst. Here, the intermediate is the free radical.
Chain propagation
Once a reactive free radical is generated, it can react with other stable molecules to form new reactive free radicals. The propagation step involves the formation of new free radicals.
Chain termination
In this step, all the intermediates or free radicals generated from the first two steps disappear and no intermediate remains.
(B) Ionic polymerization–
Ionic polymerization is defined as a type of addition polymerization in which the active centres (or intermediates) are ions or ion pairs. It can be considered as an alternative to free radical polymerization. Just like free radical polymerization, ionic polymerization also occurs in 3 steps. Since ions can be positive and negative. So depending on the positive and negative ions, ionic polymerization reactions occur in two ways: "Cationic polymerization" and "Anionic polymerization".
(1)Cationic polymerization
Cationic polymerization is defined as a type of addition ionic polymerization in which the active centres are cations. In this, the cationic initiator is used to transfer the positive charge onto the monomer molecule so that it becomes reactive. This reactive monomer reacts with other monomer molecules to form a polymer in the same way that a free radical does. Examples of polymers formed by Cationic polymerization are Poly-isobutylene (PIB), Poly-butene and Butyl rubber, etc.
(2)Anionic polymerization
Anionic polymerization is defined as a type of addition ionic polymerization in which the active centres are anions. In this, the anionic initiator is used to transfer the negative charge onto the monomer molecule so that it becomes reactive. This reactive monomer reacts with other monomer molecules to form a polymer in the same way that a free radical does. Examples of polymers formed by anionic polymerization are Synthetic Polybutadiene rubber, styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), Thermoplastic Styrene elastomers, etc.
➛ Both cationic polymerization and anion polymerization are an alternative to free radical polymerization. Therefore, it also occurs in three steps, like free radical polymerization: Chain initiation, Chain propagation and Chain termination.
Hope you have found this article helpful!!
Do you have suggestions? Please write in comment box!!!
Feel free to comment if you have any queries!!



Comments
Post a Comment