Step-Growth Polymerization Or Condensation Polymerization
In this article, we will learn about Step-growth polymerization reaction and it's characteristics in details. And also the examples of polymers formed by this step-growth polymerization process
Step-growth polymerization also known as condensation polymerization is one of the two processes of producing large molecular weight (polymer) compound from low molecular weight compound (monomers). So first of all we should know about polymerization technology, what is polymerization?
Let's understand it..........
In polymer chemistry, a reaction by which smaller molecules (called monomers) react with each other to form a larger molecule (called polymers), is called "Polymerization". Polymers are the high molecular mass compounds.
Condensation Polymerization or Step-growth Polymerization
"Step-growth polymerization reaction" also known as "Condensation Polymerization reaction".
In condensation polymerization, polymer molecules are formed by independent reactions between functional groups of a simple monomer units. In this, each step involves the combination of two polymers (or generally two different or same oligomers) of different or equal chain lengths to form a longer molecule. The reaction is a long process and the molecular mass increases very slowly.
"For the condensation polymerization reaction, the monomer compound must have at least two functional groups in its structure".
The polymers formed by condensation polymerization are copolymers in nature. In this, polymer formation occurs when some of the smaller molecules are lost as a byproduct through a reaction where the monomer molecules are joined together.
Usually, water molecules is released as a by-product.
The by-product are normally referred to as a condensate. Thus, in this polymerization technique, we get two different products: one is major product (our polymer molecule) and other one is minor project such as water, amines, alcohols, etc.
Mono-functional, bi-functional and tri-functional monomers are commonly used in this polymerization technique. Examples of polymers formed by condensation polymerization are Cellulose, Starch, Polyesters, Polyamide, Proteins, Carbohydrates, etc.
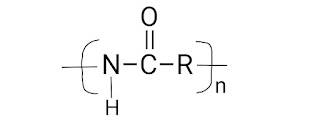
1.1 Polyamide–
Arises from the reaction between carboxylic acid (–COOH) and amine (NH₂–) groups. Examples are Nylons (Nylon-66, Nylon-6, Nylon 12, Nylon 11, etc.), Kelvar, Polyphthalamides, etc.
1.2 Polyesters–
Arises from the reaction between carboxylic acid (–COOH) and alcohol (–OH) groups. Examples are PETE/PET, terylene, etc.
1.3 Oligomers–
When a monomer reacts with some other monomer units, a polymer chain is formed that is much smaller than the original polymer chain. In a condensation polymerization reaction, each step of polymerization forms multiple polymer chains with shorter chain lengths and are called oligomers. A large number of oligomers are formed in step-growth polymerization process.
Characteristics of Polycondensation for Condensation Polymerization–
- The reaction mechanism of a polycondensation or condensation polymerization reaction is followed by the reactivity of a functional group present in the monomer unit.
- In condensation polymerization, monomer molecules should have at least two types of functional group. Like- carboxylic acid (–COOH), alcohol (–OH), aldehyde group (–CHO), amide (–NH₂), carboxylate (–COOR), etc.
- Increment of macromolecule chain or in polymeric chain is step by step process.
- No any particular active centre present in this polymerization reactions. Therefore no any initiator is required to initiate the polymerization reaction.
- Gives off small molecules as by product most commonly water.
- Forming two types of polymers structures based on the structural unit of monomer and these structures are linear (two functional groups) or cross linked or 3D structure (poly-functional groups).
- In this polymerization technique, all the monomers are quickly converted into oligomers, having shorter chain length compared to polymeric chains.
- Polymer produces by polycondensation (or condensation polymerization) reactions are low molecular weight polymers.
➛ "IUPAC" suggested the term poly-condensation instead of condensation polymerization reaction". Because polycondensation implies that the reaction is limited to condensation reaction in which small molecules such as water are expelled during polymerization while the term step polymerization or condensation polymerization encompasses not only condensation polymerization but also polymerization in which no any small molecules are expelled.
Hope you have found this article helpful!!
Do you have suggestions? Please write in comment box!!!
Feel free to comment if you have any queries!!




Comments
Post a Comment